How to Configure CORS policy for AWS S3 and CloudFront
Background
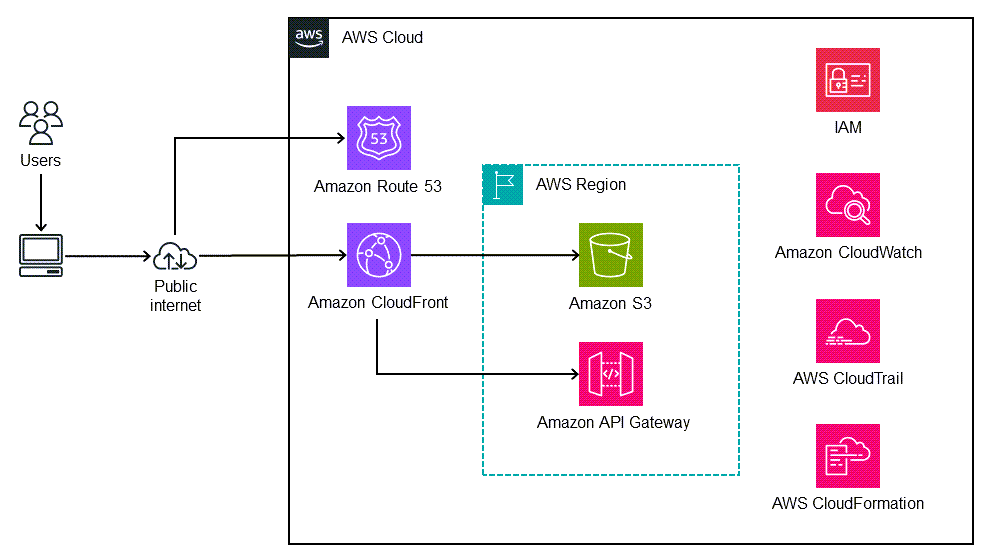 |
|---|
| source: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/prescriptive-guidance/latest/patterns/deploy-a-react-based-single-page-application-to-amazon-s3-and-cloudfront.html |
CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) configuration is crucial for web development projects, as it enables secure interaction between resources served from different domains. In this guide, we’ll delve into configuring CORS policies for AWS S3 and CloudFront to address the commonly encountered ‘blocked by CORS policy’ error. By following these steps, you can ensure seamless cross-origin requests and mitigate CORS-related issues effectively.
S3 Bucket IAM Policy
Access to XMLHttpRequest at ‘https://example.com’ from origin ‘http://localhost:3000’ has been blocked by CORS policy: No ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ header is present on the requested resource.
When encountering CORS errors like “Access to XMLHttpRequest has been blocked by CORS policy”, configuring the S3 bucket’s IAM policy is the first step to resolve them. This policy specifies which entities can access resources within the S3 bucket.
To set up the IAM policy:
- Navigate to the Permissions tab of your S3 bucket.
- Ensure that the IAM policy allows access only to CloudFront, restricting unauthorized access.
- Replace placeholders with your actual AWS account ID and CloudFront distribution information.
{
"Version": "2008-10-17",
"Id": "PolicyForCloudFrontPrivateContent",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllowCloudFrontServicePrincipal",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Principal": {
"Service": "cloudfront.amazonaws.com"
},
"Action": "s3:GetObject",
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::your-bucket-name/*",
"Condition": {
"StringEquals": {
"AWS:SourceArn": "arn:aws:cloudfront::your-account-id:distribution/your-distribution-id"
}
}
}
]
}
S3 CORS Configuration
Before jumping into configuring S3 CORS, let’s find out more about CORS itself and what it means to have it configured.
According to the AWS documentation on S3 CORS, Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) defines a way for client web applications that are loaded in one domain to interact with resources in a different domain. CORS is basically a security measure that restricts web pages from making requests to a different domain than the one that served the web application. By enabling support for CORS, you can allow these cross-origin requests by including the ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ header in responses.
Follow these steps to configure CORS for your S3 bucket:
- In the Permissions tab of your S3 bucket, locate the Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) section.
- Use the following JSON snippet as a template, adjusting the fields according to your project requirements.
- Replace “https://your-cloudfront-domain.com” with the actual CNAME of your CloudFront distribution.
[
{
"AllowedHeaders": [
"Origin",
"Access-Control-Allow-Origin",
"Content-Type",
"Accept"
],
"AllowedMethods": [
"GET"
],
"AllowedOrigins": [
"https://your-cloudfront-domain.com"
],
"ExposeHeaders": [],
"MaxAgeSeconds": 3000
}
]
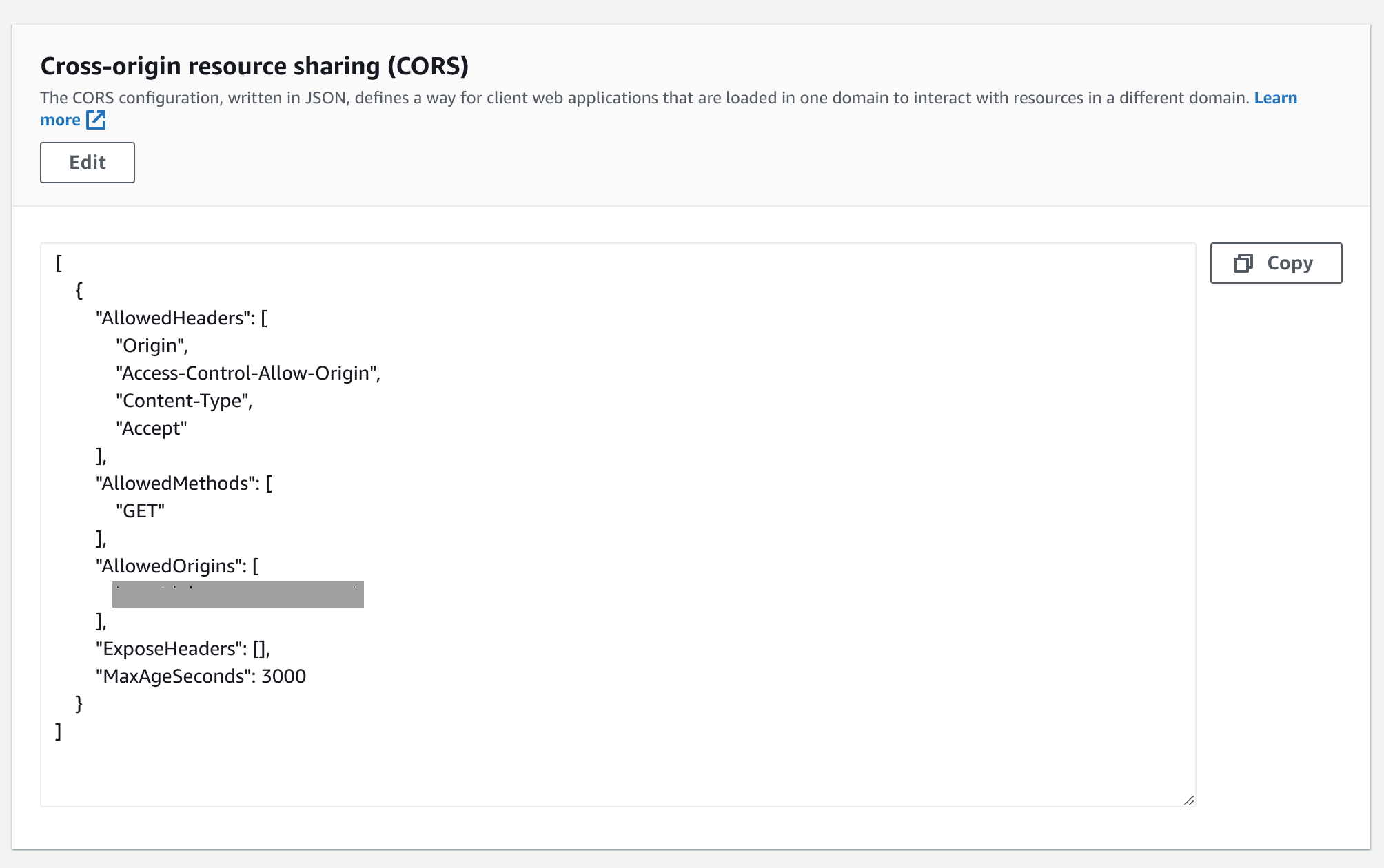
CloudFront CORS Configuration
Now let’s work on the CORS headers in our CloudFront distribution. Follow these steps:
- Navigate to your CloudFront distribution that exposes your S3 bucket
- Edit the Behavior settings and configure the necessary response headers, including the “Access-Control-Allow-Origin” header.
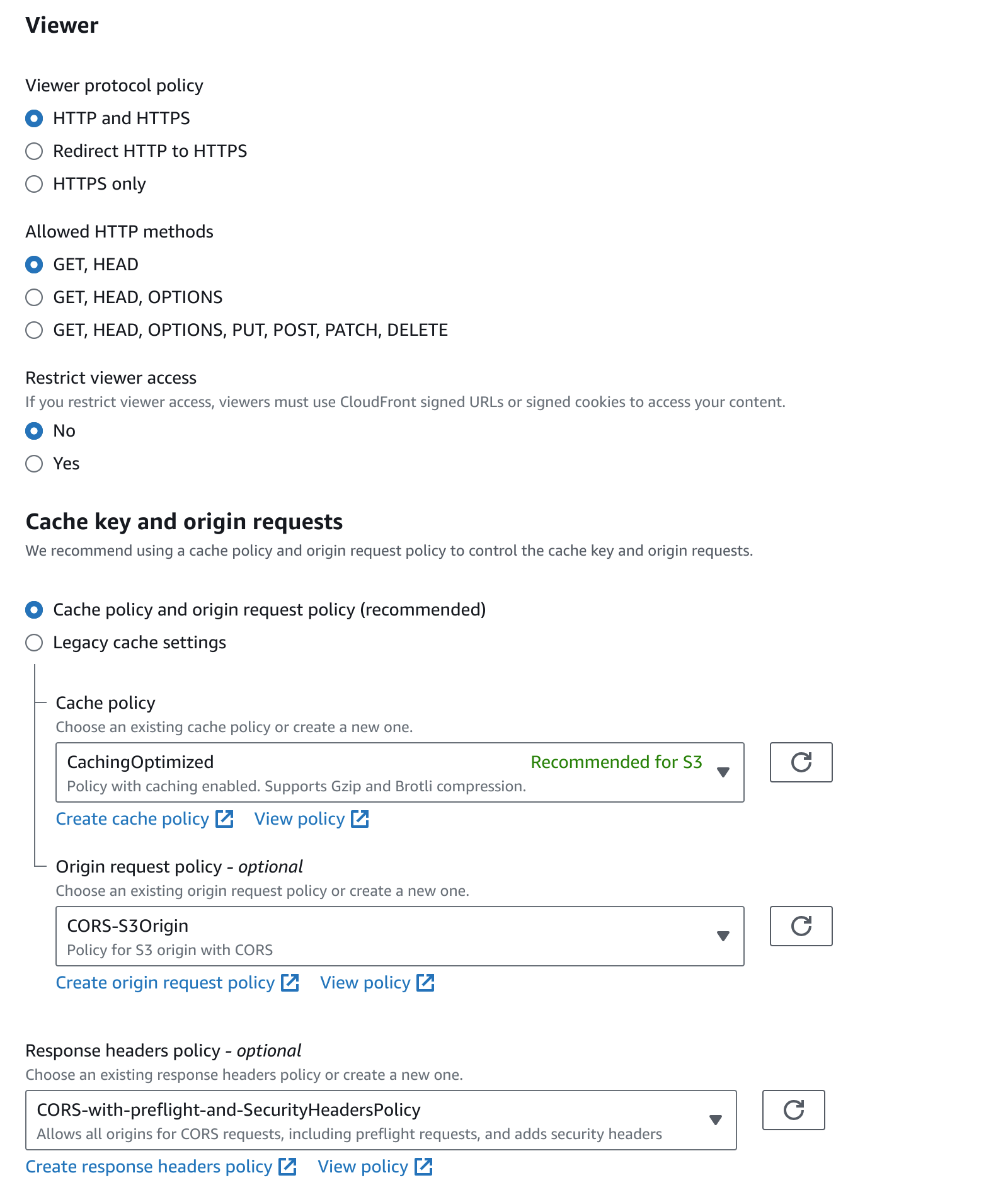
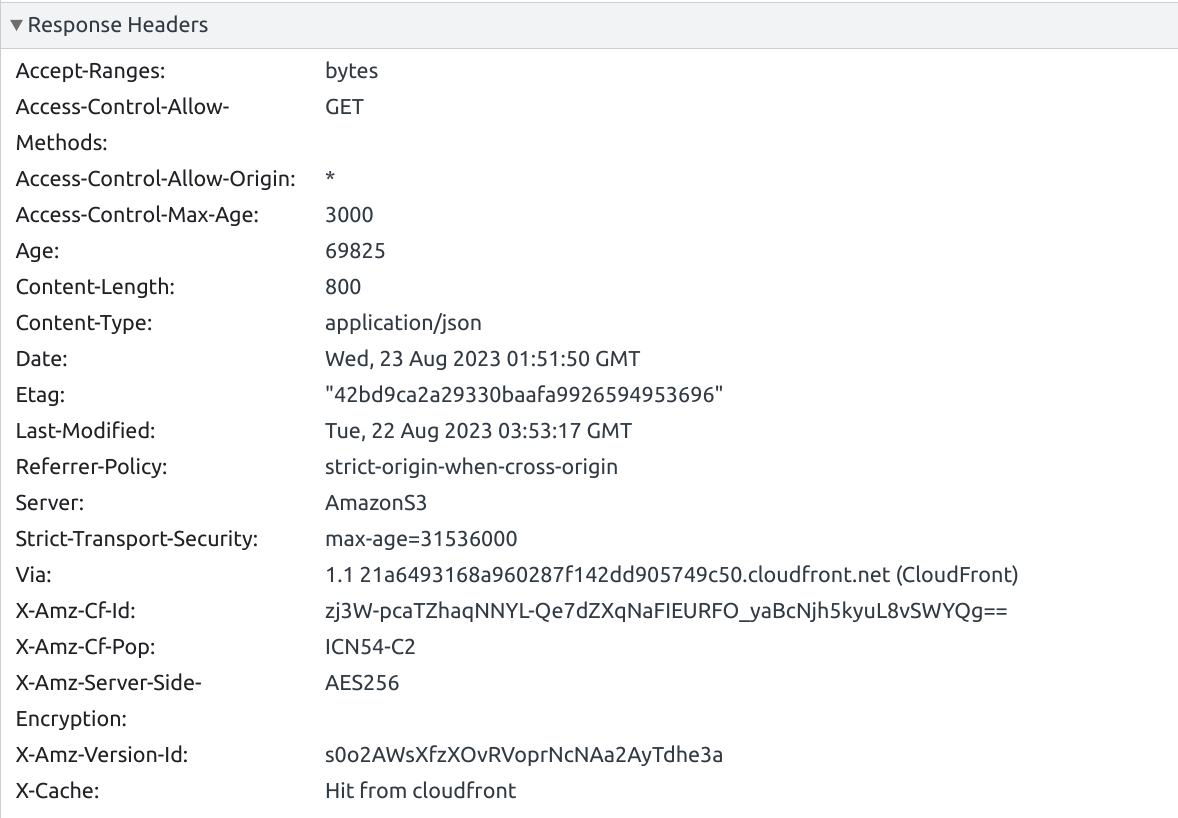
You can also go to Policies in the CloudFront console and confirm if the response headers are configured correctly.
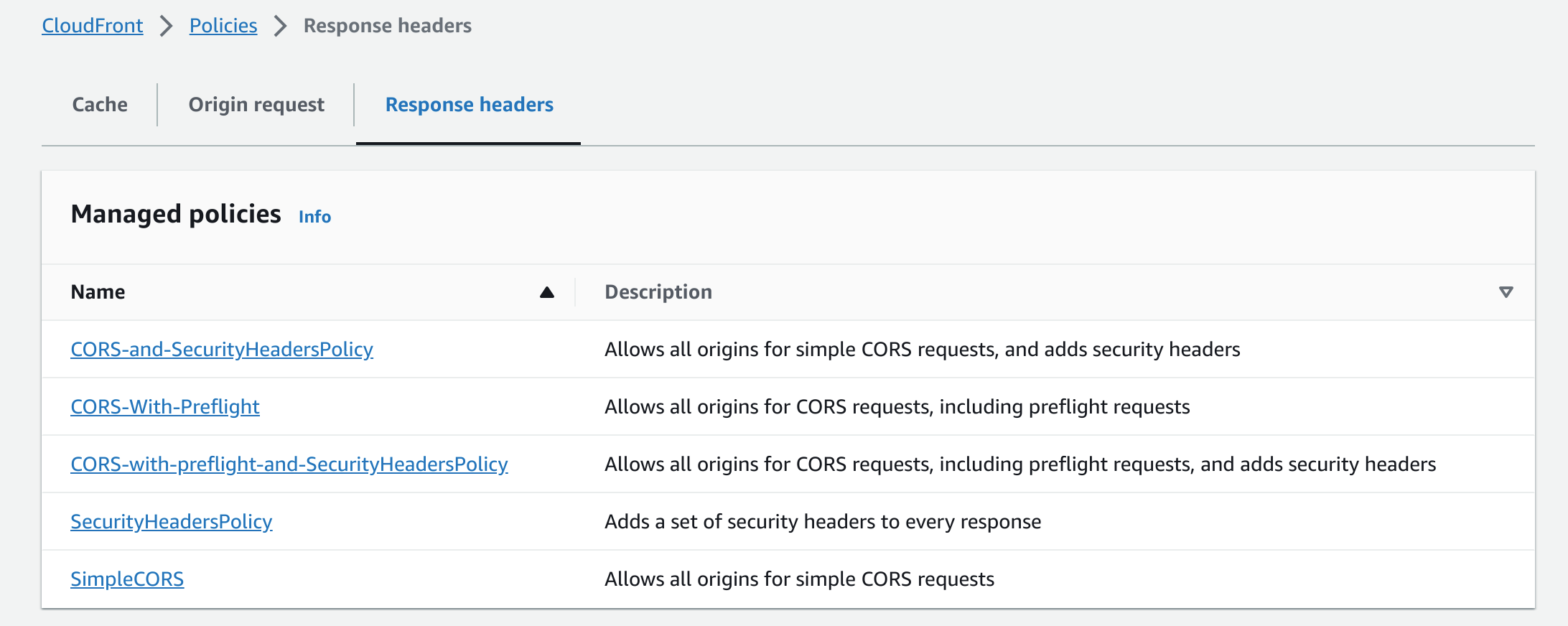
Tada! The response header includes the ‘Access-Control-Allow-Origin’ header now.

Leave a comment